Node Voltage Method
Another alternate method of analysis of multiple loop circuits is called the node voltage method. It is based on finding the voltages at each node in the circuit using Kirchhoff s current law. A node is the junction of two or more current paths.
GENERAL STEPS
The general steps for the node voltage method are as follows:
- Determine the number of nodes
- Select one node as a reference. All voltages will be relative to the reference node.
- Assign current at each node where the voltage is unknown, except at the reference node. The directions are arbitrary.
- Apply Kirchhoff s current law to each node where current are assigned.
- Express the current equations in terms of voltages and solve the equations for the unknown node voltages.
CIRCUIT FOR DEMONSTRATING NODE VOLTAGE ANALYSIS
We will use Figure-1. to illustrate the general approach to node voltage analysis.
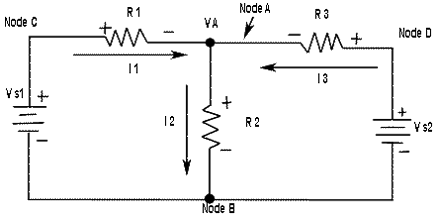
| First | Establish the node. In this case there are four nodes, as indicated in the figure. |
| Second | Let's use node B as reference. Think of it as circuit ground. Node voltages C and D are already known to he the source voltages. The voltage at node A is the only unknown it is designated as VA. |
| Third | Arbitrarily assign the currents at a node A as indicated in the figure-1 |
| Fourth | The Kirchhoff's current equation at node A is I1 - I2 + I3 = 0 |
| Fifth | Express the currents in terms of circuit voltages using Ohm's law as follow I1 = V1/R1 = (VS1 - VA)/R1 I2 = V2/R2 = VA/R2 I3 = V3/R3 = (VS2 - VA)/R3 Substituting these into the current equation, we get (VS1 - VA)/R1 -VA/R2 + (VS2 - VA)/R3 = 0 |
The only unknown is VA, so we can solve the single equation by combining and rearranging terms Once the voltage is know, all branch currents can be calculated.
EXAMPLE FOR DEMONSTRATING NODE VOLTAGE ANALYSIS
Find the node voltages in Figure
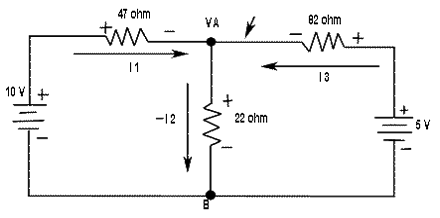
SOLUTION
The unknown node voltage is VA, as indicated in figure. This is the only unknown voltage. Currents are assigned at node A as shown. The current equation is
I1 - I2 + I3 = 0
Substitution for current using Ohm's law gives equation in terms of voltages
(10 -VA)/47 - VA/22 + (5 - VA)/82 = 0
Solving for VA yields
10/47 - VA/47 - VA/22 + 5/82 - VA/82 = 0
- VA/47 - VA/22 - VA/82 = - 10/47 - 5/82
(1804VA + 3854VA + 1034VA)/84788 = (820 + 235)/3854
6692VA / 84788 = 1055/3854
VA = (1055 X 84788)/(6692 X 3854) = 3.47 V
VA = 3.47 volt
