Digital Telephone Exchange
Digital telephone exchanges play a key role in modern telephony systems by digitizing and switching telephone calls electronically using digital computing technology. They replaced older electro-mechanical switching systems.
Key Components:
- Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC) - Convert analog voice signals to digital data.
- Digital Switching System - Uses digital logic and software to route calls between input and output ports. Employs time division multiplexing.
- Database and processors - Computerized control systems handle call processing, routing, billing etc.
- Interfaces - Connect to subscriber lines using line cards and trunk lines interconnecting exchanges.
- Power supplies - Provide stable DC power supply with battery backup.
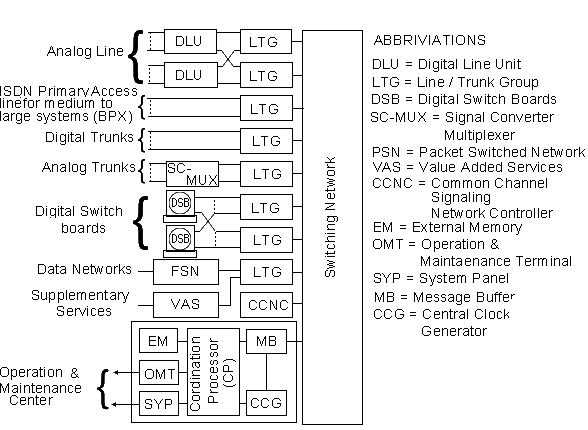
The digital Exchange includes the following Hardware Sub-System.
1- Digital Line Unite (DLU).
The DLU is connected to the LTG and it is responsible for terminating the Subscriber line and subscriber line traffic. The DLU can be installed locally or remotely, it has the following 4 primary functions.
- Conversion of the analog lines to digital.
- To accommodate the variable traffic load.
- Connection of the sub-lines.
- ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) connected.
2- Line Trunk Group (LTG)
The LTG provides the interface b/w the Digital Switching Network and the Network environment of the Exchange, which may be digital or analog .it performs the following functions.
- Receive and Transmit information on trunk and subscriber lines.
- Send Signals and Tones.
- Send and Receive messages to and from the CP.
- Adopt the transmission format to the 8 Mb/Sec highway of the switching network.
- Establish test connections.
- Display the operating status of the individual module on the LED indicator.
- Call charge registration.
- Detect fault in LTG.
- Detect fault on internal exchange interface during call processing.
3- Switching Network (SN)
All types and size of exchanges use the switching Network, The Switching Network establish a connection b/w two subscribers, belonging to Different LTG’.The Switching Network also provides a connection for the message channel, these connections are always in an indirect manner due to allowing the switches to stand-by position in case of failure one switch. Read More on Digital Networks
4- Coordination Processor (CP)
The CP handles the database as well as configuration and coordination functions, the functions are given below.
- Storage of all programs Exchanges and Sub Data.
- Connection with Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC).
- Handling of the machine interface card. In order to reduce the workload of the CP and to achieve faster processing, some processing functions are distributed over several micro-processors in the digital exchange. These functions are handled by the “CP complex” which consists of the following stages.
- Coordination Processor.
- External Memory.
- Operation and Maintenance Terminal.
- System Panel.
- Message Buffer.
- Central Clock Generator.
5- Common Channel Signaling Network Control (CCNC)
Common Channel Signaling (CCS) refers to separating signaling data from the actual voice/media path. Earlier telephone systems sent control signals over the same voice channel.
In CCS, a separate dedicated signaling channel is used to transmit all call control, routing, and other signaling information between exchanges. This is the Common Channel.
Key aspects:
- Signaling data for multiple voice circuits is multiplexed over a common channel rather than individual channels.
- This common channel uses a high-speed packet-switched data network called Signaling System 7 (SS7).
- SS7 network provides transport between CCS nodes and forms the signaling backbone.
- The voice path carries only user data, not signaling information.
Benefits:
- More efficient use of transmission capacity by separating signaling data.
- Faster and more reliable call setup and processing.
- Ability to provide advanced intelligent network services.
- Supports services like toll-free numbers, calling cards, SMS, etc.
- Enables customized services through Service Logic Programs.
- So in summary, Common Channel Signaling allows fast and efficient control signaling independent of the
- actual voice path. This enables modern intelligent telephony services.
