Ruby Laser
A ruby laser is one of the earliest types of solid-state lasers, first demonstrated in 1960 by Theodore Maiman.
Some key points in a ruby laser
- It uses a synthetic ruby rod made of aluminum oxide with a small amount of chromium ions (Cr3+) as the laser medium. The ruby rod provides the gain when pumped.
- Optical pumping is done using a bright flash lamp surrounding the ruby rod to excite the Cr3+ ions into a higher energy state.
- The excited chromium ions in the ruby emit light in the deep red range centered at 694 nm wavelength when dropping back down to lower energy states.
- The ruby rod is placed between two mirrors, including one high reflector and one partially transparent for the red ruby laser emission, forming an optical cavity.
- Lasing occurs in the ruby rod from the process of stimulated emission when photons from spontaneous chromium ion emission interact with and stimulate other excited Cr3+ ions to emit photons of the same frequency and phase.
- This amplifies the light passing repeatedly through the ruby rod between the mirrors until a high-intensity coherent laser beam emerges from the partially transparent mirror.
- Ruby lasers typically operate in pulsed mode, with short intense pulses produced using Q-switching. The pulses may have durations as short as nanoseconds.
- One of the ruby laser's distinguishing features is the bright red beam color at 694 nm, which was crucial in the early demonstration and understanding of laser physics and properties.
The ruby laser uses a chromium-doped ruby crystal pumped by a flashlamp to produce deep red laser emission at 694 nm wavelength.
Ruby belongs to the family of gems consisting of Al2O3 with various types of impurities. For example, pink Ruby contains 0.05% Cr atoms. The schematic diagram of the ruby laser can be drawn as:
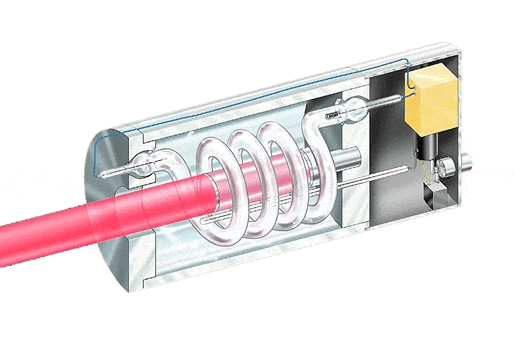
Construction of Ruby Laser
The ruby laser consists of a ruby rod, which is made of chromium-doped aluminum oxide (ruby). The rod is placed between two mirrors - one fully reflective mirror on one end and a partially reflective output coupler mirror on the other end. This forms the optical cavity.
One end of the ruby rod is mounted on an adjustable spring which allows tuning of the laser wavelength. A xenon flash lamp surrounds the ruby rod to provide optical pumping energy. The flash lamp is powered by a radio frequency (RF) power supply with switching controls to turn the lamp on and off at desired intervals.
The entire ruby rod, flash lamp and mirror assembly is contained within a sealed glass tube, usually filled with a noble gas. The RF power supply and switching electronics are mounted externally around the neck of the glass tube to control the flash lamp pulses and produce pulsed laser output.
In summary, the core ruby laser consists of the pumped ruby rod between two mirrors, contained in a glass tube with external electronics to produce pulsed optical pumping from the surrounding flash lamp. The adjustable spring end-mount allows tuning of the laser wavelength.
Operation of Ruby Laser:
When we switch on the circuit the R.F. operates. As a result, a flash of light is obtained around the ruby rod. this flash causes the electrons within the ruby rod to move from the lower energy band toward the higher energy band. The population inversion takes place at a high energy band and electrons start back to travel towards the lower energy band. During this movement, the electron emits laser light. This emitted light travels between the two mirrors where cross-reflection takes the place of this light. The stimulated laser light now escapes from the partially polished mirror in the shape of the laser beam.
The spring attached to the fully polished mirror is used to adjust the wavelength equal to λ/2 of laser light for the optimum laser beam. The switching control of the R.F. source is used to switch on and off the flashlight so that excessive heat should not be generated due to the very high frequency of the movement of the electron.
Energy Level Diagram for Ruby Laser
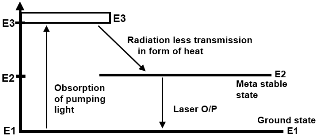
The ruby laser operates using a three-level energy system. The ground state for the chromium ions in ruby is E1. Optical pumping from the flashlamp excites the electrons into a band of closely spaced levels labeled E3 at higher energy than E1. These E3 levels are unstable and the electrons quickly decay to the intermediate meta-stable level E2.
This E2 level has a longer lifetime of around 5 milliseconds. The transition from E3 to E2 results in excess energy being given off as heat. To achieve laser action, population inversion needs to be created between the meta-stable E2 level and the ground state E1.
The flashlamp provides optical pumping to raise electrons to E3, which then rapidly decay to fill up the E2 state. Once sufficient population inversion is achieved between the higher populated E2 level and lower E1 ground state, stimulated emission can occur.
The stimulated emission from E2 to E1 produces the red 694nm laser output. The population in E2 is quickly depleted by this stimulated emission in a rapid spike lasting from nanoseconds to microseconds.
After this laser spike, the flashlamp pumping again builds up the population in E2 leading to the next pulse. This process repeats, generating an intense pulsed laser output as long as the flashlamp can maintain the required population inversion.
the three levels allow optical pumping to E3, rapid decay to fill the meta-stable E2 state, followed by stimulated emission from E2 to E1 that generates the short pulsed ruby laser output. The cycle then repeats with further pumping from the flash lamp.
Advantages:
- High power - Ruby lasers can generate pulses with very high peak power, useful for applications like drilling and cutting.
- Wavelength - The red 694 nm wavelength is strongly absorbed by many materials like metals and flesh. Good for processing and medical uses.
- Q-switching - Ruby has a long fluorescence lifetime allowing easy Q-switching to generate short, intense pulses.
- Mature technology - As one of the earliest lasers invented, ruby laser technology is very mature and well-developed.
- Cooling - Ruby has good thermomechanical properties and can be easily cooled, allowing high average power.
- Cost - Ruby lasers are relatively inexpensive compared to other high-power laser systems.
Disadvantages:
- Inefficient - Ruby has a low optical efficiency of converting pump light to laser emission, usually <1%.
- Limited tuning - The 694 nm wavelength cannot be tuned over a wide range.
- Flash lamps - Requires noisy, inefficient flash lamps for optical pumping.
- Size - Tends to be fairly large in size, especially with the pumping flashlamps.
- Pulse rate - Limited in repetition rate to a few pulses per second due to thermal effects.
- Beam quality - Beam divergence and quality are generally lower compared to other laser types.
The ruby laser's advantages lie in high peak power, Q-switching abilities, mature technology, and low cost, while disadvantages include inefficiency, limited tuning, size, and beam quality.ity of the ruby laser is short compared to other lasers, which may be considered a disadvantage.
Applications of Ruby Laser
- Material processing - Ruby lasers are used for drilling, cutting, welding, marking, and other types of material processing, especially metals. Their red beam is well absorbed by metals.
- Medical applications - In ophthalmology, ruby lasers are used for procedures like laser eye surgery. They are also used in dermatology for skin treatments like tattoos and hair removal.
- Printers - Ruby lasers provide the light source in some laser printers for exposing the drum or plate during printing.
- Instrumentation - Ruby lasers are used in laser Doppler velocimetry to measure fluid flow velocities and other motion detection instruments.
- Rangefinding - Ruby lasers can be used for optical rangefinding and lidar systems due to their high intensity, short pulses.
- Research - Ruby lasers were instrumental in early laser physics research and the development of Q-switching and mode-locking techniques.
- Holography - Ruby laser light can record holographic images due to its good coherence properties.
- Spectroscopy - The narrow emission spectrum makes ruby suitable for high-resolution spectroscopy applications.
- Optical pumping - Can be used as a light source to optically pump other laser media.
- Display technologies - Ruby lasers have been used in some laser TV and display prototypes.
Ruby laser's key roles are in materials processing, medical treatments, printing, instrumentation, rangefinding, and research - especially benefiting from its red beam wavelength, Q-switching ability, and high-intensity pulses.
