Speed of Microprocessor
The speed of microprocessor indicates that how much it is speedy to execute different programes or instructions.
There are different points which are involved in a speed of microprocessor which are explained below.
Cache built into the CPU itself is referred to as Level 1 (L1) cache. Cache that resides on a separate chip next to the CPU is called Level 2 (L2) cache. Some CPUs have both L1 and L2 cache built-in and designate the separate cache chip as Level 3 (L3) cache.
MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second)
This method explains that how much instructions are executed in one second. This method is not useful and cannot be applied because every program has a different number of instructions from another program.
Clock Frequency of Oscillator
As we know that the frequency of microprocessor operates all the functions of the functions of microprocessor so, when this frequency is low its operations will not execute faster and vice verso. The frequency of the microprocessor is indicated in MHz
Parallel Processing
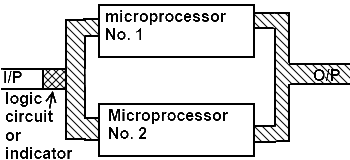
It is the architecture of microprocessor which allows the computing process to divide into two parts and to execute these parts or instructions at a time. So as the data is divided and processed by two microprocessors therefore the speed will increase.
Co-processing
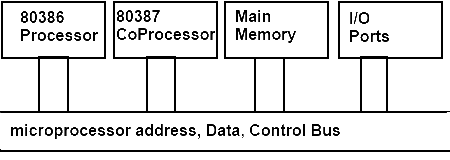
The co processing is same as parallel processing but in co-processing separate IC is used to perform some special functions. The co-processor is designed for special purpose in such a way that it completes these special functions at very high speed as compared to main processor. In this condition as the programs or instructions are executed by two processors so its speed will increase. The co-processor is connected in parallel with main processor.
Cache Memory
A very serious problem that a microprocessor faces is the low speed of main memory. As the main memory cannot give the instructions (which are used frequently) fast enough to the microprocessor, therefore another memory is used which has the capability to deliver or give these instructions very fast. This is a very fast memory which stores those instructions which are used frequently. Now the processor can take or request these instructions at very fast speed from cache memory which increases the speed of processing. Its size is normally 8 KB to 512 KB.
Cache memory is of three types or levels
- Level One
- Level Two
- Level Three
Pipe Lining
To increase the speed of the microprocessor other technique is used which called pipe is lining. In this technique a number of instruction are executed at the same time which in increases the speed of microprocessor.
Wider Buses
That microprocessor which has wider buses especially data bus automatically speeds up the processing of microprocessors. This is because of picking up many bytes as compared to one byte as in 8035.
Serial I/O (UART)
For the communication with the input and output a circuits or system is used to feed the data to microprocessor and to receive and deliver this data to output. This whole system is called serial I/O. one of the example of serial I/O which functions from series to parallel and from parallel to series. The speed of this system indicates the speed of microprocessor greater the speed, greater will be the speed of microprocessor and vice versa.
