Operational Amplifier differentiator & Integrator
Operational Amplifier differentiator
The operational amplifier is an amplifier which is directly coupled between the output and input, having a very high gain. It is used to perform a wide variety of mathematical operations like summation, subtraction, multiplication, differentiation and integration etc. in analogue computers.
An operation amplifier can be used as a differentiator as shown in Fig. 1. This circuit produces an output voltage that is proportional to the time derivative input voltage. Hence this circuit is called differentiator.
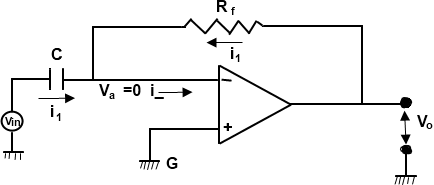
Assuming that G is virtually ground. Since the current flowing in to the virtual ground is equal to current flowing out of it we can write.
i1= if= i-1
i_ = 0
i1 = if -=0
i1 = if
from the definition of capacitance, the
charge on the capacitor is
q = CV
the charging current i is the time rate of change of charge.
Hence, output voltage V0 is equal to a constant —RC times the derivative of the input voltage Vi.
Operational Amplifier Integrator
An operational amplifier can also be used as a integrator by changing the position of R and C as shown in Fig. 2. this circuit produces an output voltage that is proportional to the time integral of the input voltage. Hence, this circuit is called an integrator.
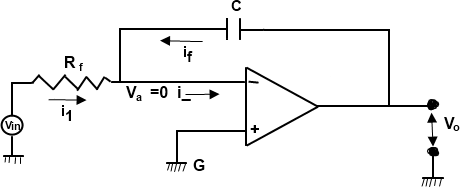
Assuming that G is virtually ground. Since the current flowing in to the virtual ground is equal to the current flowing out of it we can write.
i1+ if =i_
i_ = 0
i1+ if = 0
i1 = –if
Hence, output voltage V, is equal to a constant -1/RC times the integral of the input voltage Vi.
