Laser Accessories Part 3 (Q-Switches)
Q-Switches
The Q-Switch is a device which is placed inside the laser cavity. Main purpose of the Q-switch is to rapidly change the feedback of a laser cavity from minimum to maximum. The Q-switch blocks all feedback between the laser mirrors until the excitation mechanism has pumped the maximum energy into the active medium. Then it opens and allows maximum feedback to occur, which result in a very high peak power pulse.
Generally there are four types of Q-switches
- Mechanical Q-Switches
- Electro-optic Q-switches
- Acousto-optic Q-switches
- Chemical Q-switches
Mechanical Q-Switches
The first switch developed was a mechanical switch, which consists of prism mounted on a shaft that is turned at a high rate of speed by either electric or air motor. The prism acts as a H.R mirror in laser. The laser is pumped while prism is spinning. When the prism spins into proper alignment then feedback occurs and a pulse is generated by diagram this can be shown as:
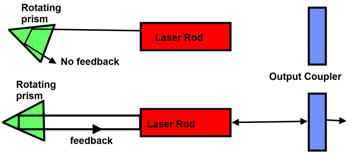
Advantages/Merits of mechanical Q-Switches
- Mechanical Q-switch construction is easy and its use with laser rod is self explanatory.
- The mechanical Q-switch consists of prism and prism acts as a HR mirror in the laser. so there is no need of another high reflectance mirror.
- From cost point of view, mechanical Q-switches are economical as compared to others.
Disadvantages/Demerits of Mechanical Q-switches:
- Mechanical Q-switches are considered to be slow by lasers standards, because it can only spin at about 25,000 rpm.
- Mechanical Q-switches requires the electric or air motor as an extra.
- Mechanical Q-switches are noisy.
- Some time mechanical Q-switches produce the undesired vibrations.
Because of these draw backs, it is rarely used nowadays.
Electro-optic Q-Switches
We know that birefringent materials have the refractive indexes different for light waves that vibrate parallel or perpendicular to their optical axis due to this reason the birefringent materials can be used to create an electro-optic Q-Switch. The electro-optic Q-switch is also called a pocket cell.
By diagram the operation of electro-optic Q-switch can be shown as:
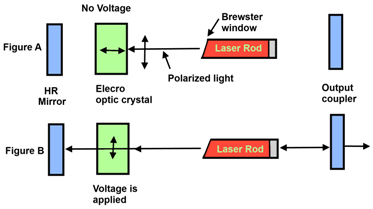
In figure A; the output of the laser rod is polarized in the vertical direction by the Brewster angle on the end of the rod. This polarized light then travels to the electro-optic crystal. Since the crystal permit only the light which is horizontally polarized to reach the H.R. mirror, so no lasing action occurs. At this time, the active medium can be pumped to its maximum energy level and no output pulse obtained.
In figure B; we apply simply a voltage across the electro-optic crystal. This causes the crystal to change its direction of polarization and permits the vertically polarized light to reach the H.R. mirror. The light is then reflected back into the active medium and lasing action occurs. At this time the output pulse is obtained.
Advantages / Merits of Electro-optic Q-Switches
- These switches are faster than mechanical switches.
- These switches are also not noisy.
- From cost point of view they are not much more costly.
- These switches do not produce any vibrations.
Disadvantages / Demerits of Electro-optic Q-Switches
- Their construction as well as explanation is slight difficult.
- Since they are faster than mechanical Q-switches but are slower than acousto-optic Q-switches.
- Voltage need for electro-optic crystal can be considered its disadvantage.
Acousto-optic Q-Switches
The refractive index of the some materials such as quartz will change when mechanical pressure is applied. This change in refractive index causes incident light to bend differently as it passes through the material.
An acousto-optic Q-switches operates on this principle. By applying shock waves to the crystal, areas of the increased and reduced refraction are created. When a beam traveling through the crystal, encountering these changes in refractive indeed, the beam is bent. If the crystal is placed between the laser mirrors then beam is bent out of the alignment. So that feedback cannot occur and so no output obtained.
If now the mechanical pressure Is stopped. Then beam will go in alignment so the feedback occurs and as a result the output is obtained.
Remember that the shock waves (used to flex the crystal) are produced by a RF (radio frequency) generator which applies an alternating voltage to transducer. The transducer vibrates in response to the applied voltage. Since it is adhered to the crystal, therefore the vibrations are transmitted into the crystal.
Advantages / Merits of Acousto-optic Q-Switches
- Q-switch can be very fast with this system. It is possible to produce laser pulses at rate of 25000 pulses per second, when an acousto-optic Q-switch is used in conjunction with continuous laser pumping system.
- These Q-switches produce no noise during their action or operation.
- Crystal use instead of prism is usually preferred.
Disadvantages / Demerits of Acousto-optic Q-Switches
- It requires the RF generator for production of shock wave, which are used to flex crystal.
- The cost of acousto-optic Q-switches is more than mechanical Q-switches.
Chemical Q-Switches
There are many types of the organic chemical dyes which change their absorption properties from opaque to transmissive when exposed to intense light.
To Q-switch a laser with bleachable dye, the dye is mixed in a solvent to the proper concentration or the dye is formulated in plastic disk.
A container with the liquid dye or the plastic disk is placed between the laser mirrors. Then the laser is pumped the surface of the dye container is slightly reflective and allow some feedback to occur even though laser light has not penetrated the dye to form an output beam. The feedback (small as it is) increases but most of its energy is absorbed in the dye. When the pumping level is high enough that the dye can no longer absorb the small laser output then the dye bleaches and turns transparent to the laser wavelength. An output pulse is generated and the dye returns to its absorptive condition.
The concentration of liquid dye or the thickness of the plastic dye disk determines the amount of energy needed to bleach the dye and thus determines when the laser pulse occurs.
Advantages / Merits of Chemical Switches
- In chemical Q-switches organic dye goes through its bleaching cycle very rapidly, that is why these can also be used to mode lock a laser.
- The chemical Q-switches are not noisy.
- These types of switches does not produce any vibrations.
