Stereo Broadcast Transmission
Stereo broadcast transmission is a method of transmitting audio signals in stereo, providing listeners with a more immersive and realistic audio experience. Unlike mono transmission, which uses a single audio channel, stereo transmission utilizes two separate audio channels to reproduce sound from different directions. This article explores the significance of stereo sound, the evolution of stereo broadcast transmission, different transmission technologies, encoding techniques, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
The Importance of Stereo Sound
Stereo sound has become an integral part of our lives, enriching our audio experiences across various mediums. Whether we are listening to music, watching movies, or enjoying radio broadcasts, stereo sound adds depth, dimension, and realism to the audio content. It allows us to perceive the placement and movement of sound sources, creating a more engaging and immersive auditory environment.
Evolution of Stereo Broadcast Transmission
The journey of stereo broadcast transmission dates back several decades. In the early days of radio, mono transmission was the norm. However, with advancements in technology and the demand for high-quality audio, stereo transmission gained popularity. The first stereo FM radio broadcasts began in the 1960s, revolutionizing the way people experienced audio content. Since then, stereo transmission has evolved significantly, keeping pace with advancements in broadcasting technologies.
Stereo Transmission Technologies
There are several technologies used for stereo broadcast transmission. FM radio remains a widely used medium for stereo transmission, especially in terrestrial broadcasting. FM radio broadcasts provide good audio quality and coverage, making it accessible to a wide audience. In addition to FM, digital radio platforms have also adopted stereo transmission, offering enhanced sound quality and additional features.
With the rise of the internet, online streaming platforms have emerged as a popular medium for stereo broadcast transmission. Internet radio stations and music streaming services deliver stereo audio content to listeners worldwide, providing convenient access to a vast range of music genres and radio shows.
Stereo Encoding Techniques
To transmit stereo audio, encoding techniques are employed to compress and efficiently transmit the audio signals. In analog stereo encoding, the left and right audio channels are combined into a composite signal using different encoding methods, such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM). These encoded signals are then transmitted through the broadcasting medium.
In digital stereo encoding, the audio signals are converted into a digital format and encoded using various algorithms. The encoded signals are then transmitted digitally, ensuring high fidelity and precise reproduction of the original audio content. Digital encoding techniques offer better signal quality and resistance to noise compared to analog methods.
Benefits
The stereo broadcast transmission offers numerous benefits to both broadcasters and listeners. Firstly, it enhances the listening experience by creating a sense of spaciousness and depth in the audio. It allows for the accurate placement of sound sources, making the listening experience more immersive and engaging.
Secondly, stereo transmission enables realistic sound reproduction. It captures the nuances of the original audio recording, preserving the artist's intended spatial effects and creating a lifelike representation of the soundstage.
Furthermore, stereo broadcast transmission provides artists and audio engineers with a powerful tool for artistic expression. By utilizing stereo panning and spatial effects, they can create dynamic and captivating audio productions, enriching the overall artistic experience for the audience.
Challenges and Limitations of Stereo Transmission
While stereo broadcast transmission offers significant advantages, there are also challenges and limitations to consider. Signal quality and interference can affect the overall audio experience. Factors such as atmospheric conditions, signal obstructions, and electromagnetic interference can impact the clarity and stability of the stereo signal.
Additionally, equipment compatibility is crucial for ensuring seamless stereo reception. Different devices and receivers may have varying capabilities and decoding algorithms, which can affect the quality of the reproduced sound.
Furthermore, listener preferences play a role in stereo transmission. Some listeners may prefer mono audio for certain types of content or due to personal preferences. Balancing the demand for stereo content while catering to different listener preferences can be a challenge for broadcasters.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of stereo broadcast transmission holds exciting possibilities. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in audio quality, transmission efficiency, and compatibility. The development of immersive audio technologies, such as 3D audio and binaural rendering, may further enhance the stereo experience, creating a more realistic and captivating auditory environment.
Block Diagram
A block diagram of a typical frequency stabilizing system used is shown in Figure. It uses a basic frequency, a Standard, and a crystal oscillator, and the carrier frequency of the FM signal is compared; with it. We know that the reactance modulator works across the tank circuit of an LC oscillator, whose output is isolated by a buffer stage. The output of the buffer is fed to an amplitude limiter and subsequently to the class C power amplifiers (not shown).
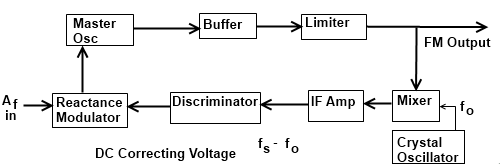
A small portion of the signal is taken from the limiter output and fed to the mixer in which this signal is mixed with a signal from the crystal oscillator. The difference signal which is usually about one-tenth- to one-twentieth of the master oscillator frequency is amplified and applied to a phase discriminator. The output of the phase discriminator is a DC signal which is applied to the reactance modulator as a correcting voltage to counteract any drift in the average frequency of the master oscillator.
The discriminator is so designed that it reacts to slow changes in the incoming frequency, but not to the normal frequency variation due to frequency modulation. Also, the discriminator provides a positive 0/p voltage if the input frequency exceeds the discriminator-tuned frequency and 0 a negative 0/p voltage if it is lower.
Stereo Broadcast Transmission
A stereo signal consists of two channels which can be labeled L and R (left and right), one channel for each speaker. The ordinary mono signal consists of the summation of the two channels, i.e. L + R, and this can be transmitted in the normal way. If a signal containing the difference between the left and right channels, L - -R, is transmitted then it is possible to reconstitute the left and right only signals. By adding the stun and difference signals i.e. (L + R) + (L – R), gives 2L, i.e. the left signal.
and subtracting the two signals, i.e.(L + R) – (L – R) gives 2R, the right signal. This can be achieved relatively simply by adding and subtracting signals electronically. It only remains to find a method of transmitting the stereo difference signal in a way that does not affect any mono receivers.
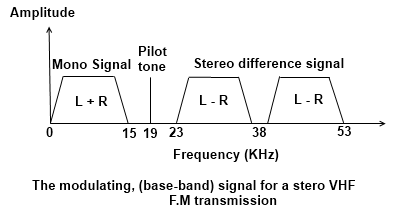
This is achieved by transmitting the difference signal above the audio range. It is amplitude modulated onto a 38 KHz sub-carrier. Both the upper and lower side-bands are retained, but the 38 kHz sub-carrier itself is suppressed to give a double side-band signal above the normal audio bandwidth as shown in Figure This whole base-band is used to frequency modulate the final radio frequency carrier.
To regenerate the 38 KHz sub-carrier, a 19 kHz pilot tone is transmitted. The frequency of this is doubled in the receiver to give the required 38 KHz signal to demodulate the double side-band stereo difference signal. The frequency of the pilot tone is also used to detect whether a stereo signal is being transmitted. If it is not
present, the stereo reconstituting circuitry is turned off. Forever, when it is present, the stereo signal can be constituted.
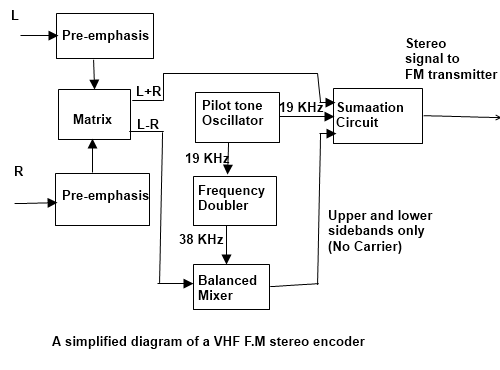
To generate the stereo signal, a system similar to that shown in Figure is used. The left and right signals enter the encoder where they are passed through a circuit to add the required pre-emphasis. After this, they are passed into a matrix circuit. This adds and subtracts the two signals to provide the L + R and L — R signals. The L + R signal is passed straight into the final summation circuit to be transmitted as the ordinary mono audio, The difference L — R signal is passed into a balanced modulator to give the double side-band suppressed carrier signal centered on 38 KHz. This is passed into the final summation circuit as the stereo difference signal. The other signal entering the balanced modulator is a 38 KHz signal which has been obtained by doubling the frequency of the 19 KHz pilot
Tone. The pilot tone itself is also passed into the final summation circuit. The final modulating signal consisting of the L + R mono signal, 19 KHz pilot tone, and the L – R difference signal based around 38 KHz is then used to frequency modulate the radio frequency carrier before being transmitted.
Conclusion
Stereo broadcast transmission has transformed the way we experience audio content. With its ability to reproduce sound from multiple directions, stereo sound adds depth, realism, and artistic expression to music, movies, and radio broadcasts. While challenges exist, the benefits and potential for future advancements make stereo transmission a significant aspect of the audio industry.
